Dog 8 in Human Years embarks on an enlightening journey into the fascinating world of canine aging, exploring the intricacies of a dog’s lifespan and the remarkable bond between humans and their beloved companions.
Delving into the science behind dog years, we unravel the mysteries of their accelerated aging process, providing a comprehensive understanding of how to care for our furry friends as they gracefully navigate the golden years.
Understanding Dog Years
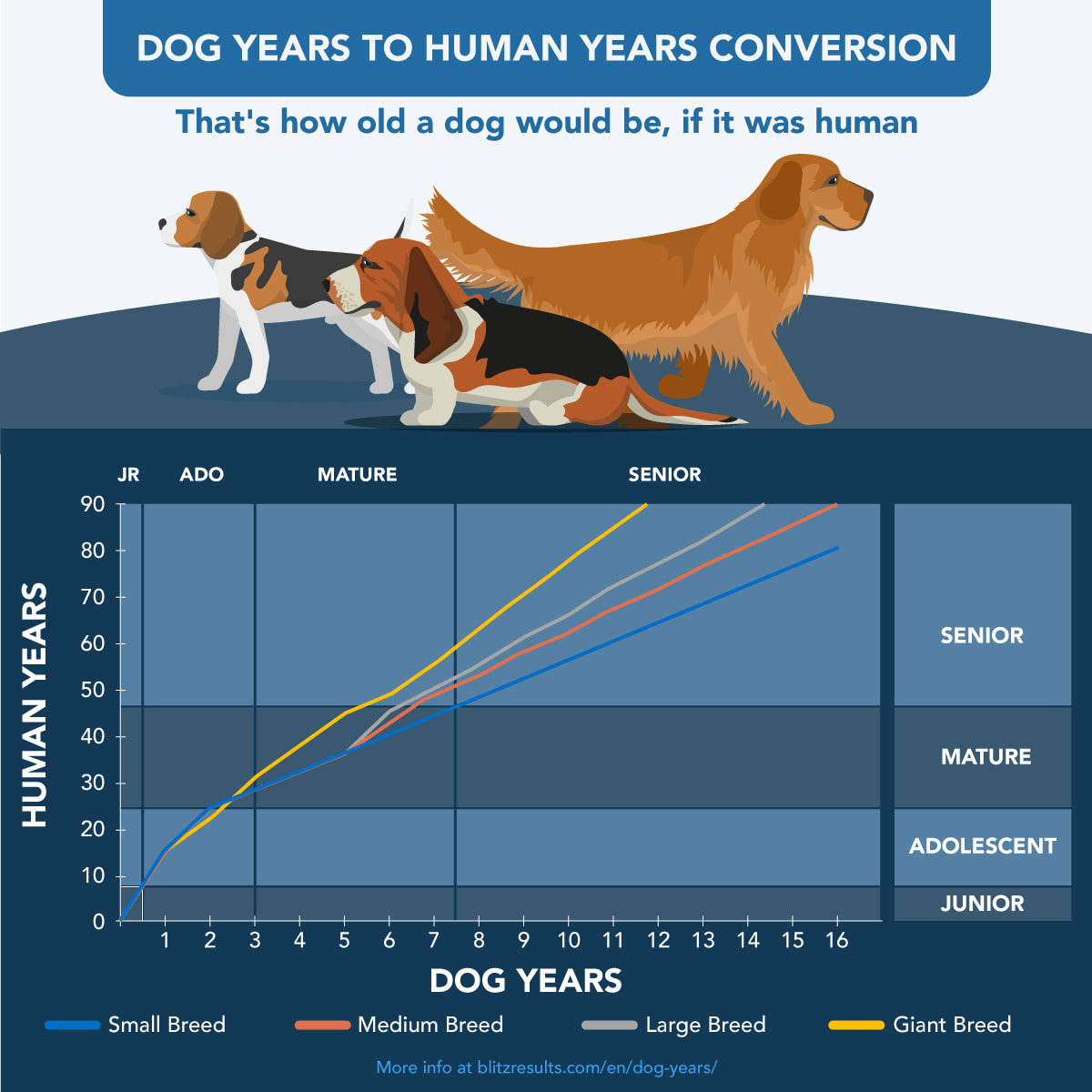
The concept of “dog years” is a simplified way of comparing the aging process of dogs to that of humans. While dogs and humans both experience a similar sequence of developmental stages, the rate at which they age differs significantly.
A common rule of thumb is that one human year is equivalent to seven dog years. However, this ratio is not always accurate and can vary depending on the breed, size, and overall health of the dog.
Formula for Converting Dog Years to Human Years
A more precise formula for converting dog years to human years is as follows:
Human Years = 16 + (Dog Years
- 11)
- 4
For example, a 5-year-old dog would be approximately 33 human years old using this formula.
Factors Affecting a Dog’s Aging Process
Several factors can affect the aging process of dogs, including:
- Breed: Larger breeds tend to have shorter lifespans than smaller breeds.
- Size: Smaller dogs generally live longer than larger dogs.
- Health: Dogs with chronic health conditions may age more quickly.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet can help promote a dog’s longevity.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help keep dogs healthy and active.
Health and Aging
The lifespan of dogs varies widely by breed, with smaller breeds generally living longer than larger breeds. The average lifespan of a dog is between 10 and 13 years, but some breeds can live for as long as 15 or even 20 years.
As dogs age, they undergo a number of physical and mental changes. These changes can include:
Physical Changes
- Graying of the muzzle and hair
- Loss of muscle mass and strength
- Stiffness in the joints
- Reduced mobility
- Increased susceptibility to infection
Mental Changes, Dog 8 in human years
- Cognitive decline
- Reduced learning ability
- Changes in sleep patterns
- Increased anxiety or irritability
Common Health Issues Associated with Aging Dogs
As dogs age, they are more likely to develop a number of health issues, including:
- Arthritis
- Cancer
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
It is important to take your dog to the veterinarian for regular checkups as they age. This will help to ensure that any health problems are detected and treated early on.
Cognitive Changes: Dog 8 In Human Years
As dogs age, they may experience cognitive changes similar to those seen in humans. These changes can affect their memory, learning ability, and spatial awareness.Common cognitive changes in aging dogs include:
-
-*Disorientation
Dogs may become confused or disoriented in familiar places.
-*Memory loss
Dogs may forget commands or have difficulty remembering people or places.
-*Reduced learning ability
Dogs may take longer to learn new things or may not be able to learn new things at all.
-*Changes in sleep-wake cycles
Dogs may sleep more or less than usual, or they may have difficulty sleeping at night.
-*Changes in appetite
Dogs may eat more or less than usual, or they may become picky about their food.
-*Changes in behavior
Dogs may become more withdrawn or less social, or they may exhibit repetitive behaviors such as pacing or licking.
Recognizing and Addressing Cognitive Changes
It is important to recognize the signs of cognitive changes in your dog so that you can address them appropriately. If you notice any changes in your dog’s behavior, consult with your veterinarian to rule out any underlying medical conditions.There
are a number of things you can do to help your dog cope with cognitive changes:
-
-*Provide a safe and familiar environment
Keep your dog’s home environment as familiar and predictable as possible. Avoid making major changes to the furniture or routine.
-*Establish a regular routine
Dogs with cognitive changes benefit from a regular routine that provides them with structure and predictability. Feed them at the same time each day, take them for walks at the same time each day, and play with them at the same time each day.
-*Provide mental stimulation
Dogs with cognitive changes need mental stimulation to keep their minds active. Play games with them, teach them new tricks, or take them for walks in new places.
-*Be patient and understanding
Dogs with cognitive changes may not be able to do things that they used to be able to do. Be patient and understanding, and don’t get frustrated if they make mistakes.
Maintaining a Dog’s Mental Health as They Age
In addition to the above tips, there are a number of other things you can do to help maintain your dog’s mental health as they age:
-
-*Socialize your dog
Dogs need social interaction to stay mentally healthy. Make sure your dog has plenty of opportunities to interact with other dogs and people.
-*Exercise your dog
Exercise is not only good for your dog’s physical health, but it is also good for their mental health. Exercise helps to release endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects.
-*Feed your dog a healthy diet
A healthy diet is essential for your dog’s overall health, including their mental health. Feed your dog a diet that is high in quality and low in processed ingredients.
-*Take your dog to the veterinarian for regular checkups
Regular veterinary checkups are important for detecting and treating any underlying medical conditions that could affect your dog’s mental health.
Care and Management
As dogs age, their needs and care requirements change. Providing proper care and management is essential for ensuring their well-being and comfort.
Nutrition
Dietary modifications may be necessary as dogs age. Senior dogs often have reduced appetites and digestive sensitivities. They may also have difficulty chewing, requiring softer foods or supplements. Consult with a veterinarian to determine the best diet for your aging dog.
Exercise
Regular exercise is still important for aging dogs, but the intensity and duration should be adjusted. Opt for low-impact activities such as short walks, swimming, or interactive games. Avoid strenuous activities that could put stress on their joints.
Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for aging dogs. Senior dogs are more prone to health issues, and early detection and treatment can improve their quality of life. Discuss any changes in behavior, appetite, or mobility with your veterinarian promptly.
Comfortable Environment
Creating a comfortable and supportive environment is essential for aging dogs. Provide them with soft bedding, ramps or stairs for easy access to furniture, and a quiet space where they can rest. Ensure their surroundings are safe and free from hazards.
Behavioral Changes
Aging dogs may experience behavioral changes, such as increased anxiety, confusion, or incontinence. Patience and understanding are key. Provide a calm and reassuring environment, and consult with a veterinarian or animal behaviorist if necessary.
Euthanasia
Euthanasia is the act of intentionally ending a life to relieve pain and suffering. It is a difficult decision that pet owners may face when their dog is terminally ill or has a poor quality of life.The decision to euthanize a dog is a personal one that should be made in consultation with a veterinarian.
There are a number of factors to consider, including the dog’s age, health, quality of life, and the owner’s financial and emotional resources.
Methods of Euthanasia
There are several different methods of euthanasia that can be used for dogs. The most common method is intravenous injection of a barbiturate, which quickly and painlessly stops the heart. Other methods include inhalation of carbon dioxide, injection of a potassium chloride solution, and electrocution.Each
method of euthanasia has its own pros and cons. Intravenous injection of a barbiturate is the most common method because it is quick and painless. However, it can be more expensive than other methods. Inhalation of carbon dioxide is also a quick and painless method, but it can be more difficult to administer.
Injection of a potassium chloride solution is a less expensive method, but it can be more painful than other methods. Electrocution is the least common method of euthanasia because it can be more dangerous and painful.It is important to discuss the different methods of euthanasia with a veterinarian before making a decision.
The veterinarian can help the owner choose the method that is most appropriate for their dog.
Support and Grief Counseling
Euthanasia is a difficult decision that can lead to feelings of grief and loss. There are a number of resources available to help pet owners cope with the loss of their dog. These resources include pet loss hotlines, support groups, and grief counselors.Pet
loss hotlines provide immediate support to pet owners who are grieving the loss of their dog. Support groups allow pet owners to connect with other people who have experienced the loss of a pet. Grief counselors can help pet owners to process their grief and to develop coping mechanisms.
Closure
As we conclude our exploration of dog 8 in human years, let us cherish the profound connection we share with our canine companions. By embracing their unique aging journey, we honor their unwavering loyalty and celebrate the indelible paw prints they leave on our hearts.
Query Resolution
How can I calculate my dog’s age in human years?
The general rule is to multiply your dog’s age by 7 during their first two years of life, then add 5 for each additional year.
What factors influence a dog’s aging process?
Breed, size, diet, exercise, and overall health all play a role in determining a dog’s lifespan and aging trajectory.
What are common health issues associated with aging dogs?
Arthritis, cognitive decline, heart disease, and cancer are among the most prevalent health concerns in senior dogs.
How can I provide the best care for my aging dog?
Regular veterinary check-ups, a nutritious diet, gentle exercise, and a comfortable living environment are essential for maintaining your dog’s well-being in their later years.