Dog 6 in Human Years: Unveiling the Secrets of Canine Aging takes a deep dive into the fascinating relationship between the ages of dogs and humans, exploring the factors that influence conversion, the practical applications of this knowledge, and the cultural perspectives that shape our understanding of our canine companions.
As we delve into this topic, we will uncover the intricacies of dog years and their human equivalents, gaining insights into the health and well-being of our beloved pets.
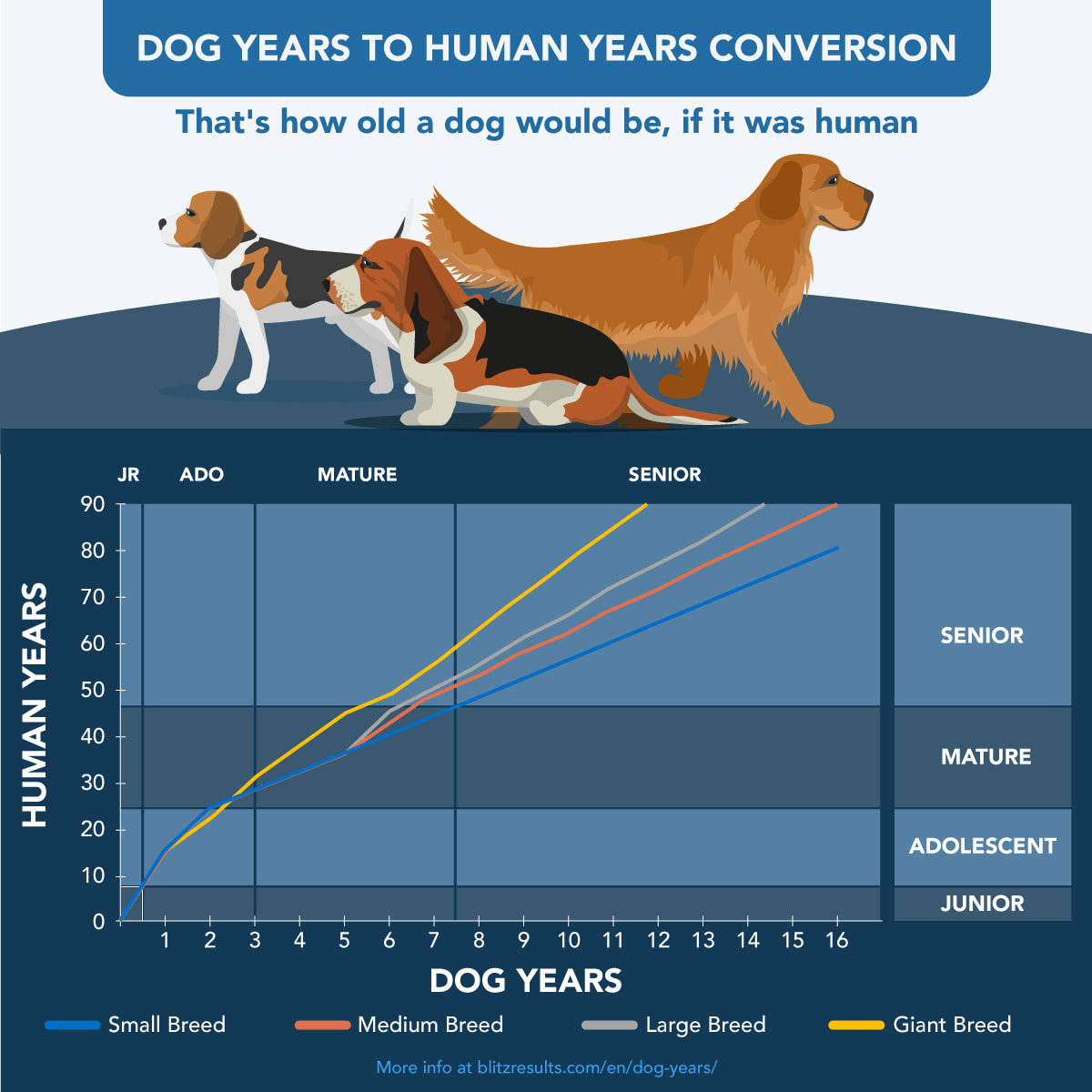
Age Conversion
Determining the human age equivalent of a dog’s age is a common topic of interest for pet owners. While there is no exact formula that applies to all dogs, due to variations in breed, size, and overall health, there are general guidelines that can provide a rough estimate.
Age Conversion Table
The following table provides approximate human age equivalents for different dog ages:
| Dog Age (Years) | Human Age Equivalent (Years) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 15 |
| 2 | 24 |
| 3 | 28 |
| 4 | 32 |
| 5 | 36 |
| 6 | 40 |
| 7 | 44 |
| 8 | 48 |
| 9 | 52 |
| 10 | 56 |
Factors Affecting Conversion
The conversion of dog years to human years is not a straightforward calculation and can vary based on several factors. These factors include breed, size, and health.
Breed
Different breeds of dogs have different life expectancies and developmental rates. For example, smaller breeds, such as Chihuahuas, tend to live longer than larger breeds, such as Great Danes. This difference in life expectancy is reflected in the conversion factor used to calculate dog years to human years.
Size
The size of a dog can also affect the conversion factor. Larger dogs tend to have shorter life expectancies than smaller dogs. This is because larger dogs are more prone to certain health problems, such as hip dysplasia and heart disease.
Health
The overall health of a dog can also affect the conversion factor. Dogs that are healthy and well-cared for tend to live longer than dogs that are sick or neglected. This is because healthy dogs are less likely to develop health problems that can shorten their life expectancy.
Life Expectancy: Dog 6 In Human Years
The average life expectancy of dogs varies widely depending on breed, size, and overall health. However, on average, dogs live for approximately 10-13 years, while humans live for around 72-83 years.
The conversion of dog years to human years can provide insights into a dog’s overall health and well-being. For instance, a 10-year-old dog is considered a senior citizen, while a 10-year-old human is still relatively young. This conversion helps us understand that dogs age at a faster rate than humans and may require additional care and attention as they get older.
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
- Breed:Certain breeds, such as giant breeds, tend to have shorter lifespans than smaller breeds.
- Size:Smaller dogs generally live longer than larger dogs.
- Diet and Exercise:A healthy diet and regular exercise can contribute to a longer life expectancy.
- Genetics:Some genetic conditions can affect a dog’s lifespan.
- Environmental Factors:Exposure to toxins or pollutants can shorten a dog’s life.
Practical Applications

The conversion of dog years to human years has several practical applications, particularly in veterinary medicine and pet care. Understanding the equivalent age of a dog in human years allows veterinarians and pet owners to make informed decisions about their pet’s health and well-being.
Spaying and Neutering, Dog 6 in human years
Determining the appropriate age for spaying or neutering a dog is crucial for their overall health and behavior. The conversion formula can help estimate the human age equivalent of a dog, which can be used as a guide for when to schedule these procedures.
For example, the optimal age for spaying or neutering small breeds is typically around 6 months, which corresponds to approximately 14 human years. Larger breeds, on the other hand, may need to wait until they are 9-12 months old, which is equivalent to 21-28 human years.
Ethical Implications
While the conversion of dog years to human years can be a useful tool, it is important to consider the ethical implications of using it to make decisions about a dog’s life. The conversion should not be used to determine a dog’s “expiration date” or to make decisions about euthanasia.
Dogs are sentient beings with their own unique experiences and perspectives, and their lives should be valued and respected regardless of their age in human years.
Cultural Perspectives

Different cultures have unique perspectives on the relationship between dog years and human years, shaping how people interact with and care for their canine companions.
In many Western cultures, the traditional conversion of one dog year to seven human years has been widely accepted. This belief stems from the observation that dogs typically reach physical maturity faster than humans, with smaller breeds maturing sooner than larger ones.
Variations in Conversion Ratios
However, cultural variations exist in the conversion ratios used. For instance, in some Asian cultures, the conversion ratio is often one dog year to ten human years. This difference reflects the cultural emphasis on respecting elders and recognizing the wisdom gained with age.
Impact on Dog Care
These cultural perspectives influence how people approach dog care. In cultures where the conversion ratio is higher, dog owners may prioritize early socialization and training to ensure their dogs adapt well to human society during their shorter perceived lifespan.
Conversely, in cultures with a lower conversion ratio, dog owners may place greater emphasis on providing extended care and support for their dogs, recognizing their longer perceived companionship.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the conversion of dog years to human years provides a valuable tool for understanding our canine companions, their health, and their place in our lives. By considering the factors that influence conversion and the cultural perspectives that shape our interactions with dogs, we can foster deeper connections and provide the best possible care for our furry friends.
Commonly Asked Questions
How accurate is the conversion of dog years to human years?
The conversion is an approximation, as there is no exact formula that applies to all dogs. However, it provides a general guideline for understanding a dog’s developmental stages and health status.
What factors influence the conversion of dog years to human years?
Factors such as breed, size, and health can impact the conversion. Smaller breeds tend to have longer life expectancies and age more slowly than larger breeds.
How can I use the conversion to make decisions about my dog’s care?
The conversion can help you determine the appropriate age for spaying or neutering, vaccinations, and other preventive care measures. It can also provide insights into your dog’s overall health and well-being.